Advanced Parametric Design with Grasshopper
Design Inspiration
Rhino+Grasshopper is a fantastic combination. I am totally obsessed with it. Here on Project 2, I am going to utilize some of the advanced parameter modeling tools in Grasshopper.
The atrium has become an important design feature for many buildings. This project is to study the indoor condition of an atrium, including solar irradiation, thermal comfort, etc.
1`3K8P0{}}4FKNS)V6EC.jpg)
As we can see, the atriums showed in these two photos have a circle shaped skylight. I believe if we change the orientation, size, and angle of the round skylight roof, we can get different results for the indoor environment.
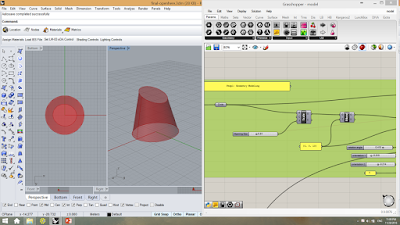
Therefore, I built a base-case model or stereotype model in Grasshopper. It is a loft space with round skylight.
Performance Driven Design: Daylighting Simulation and Optimization
• •
This is the original shape of the model. Basically, I have set several parameters for this model, in order to change the size of the skylight, the orientation of the roof, and the rotation angle of the roof.
• EnergyPlus • • Psychrometric
• Lunchbox •
We can use Lunchbox to generate the patterns for the walls. If we want to design a panel, and have that panel all over on to the walls in a certain way, we also need Panelingtools to do that.
floor tiles 2
floor tiles 3
floor tiles 4
Project Movie
Rhino+Grasshopper is a fantastic combination. I am totally obsessed with it. Here on Project 2, I am going to utilize some of the advanced parameter modeling tools in Grasshopper.
The atrium has become an important design feature for many buildings. This project is to study the indoor condition of an atrium, including solar irradiation, thermal comfort, etc.
1`3K8P0{}}4FKNS)V6EC.jpg)
As we can see, the atriums showed in these two photos have a circle shaped skylight. I believe if we change the orientation, size, and angle of the round skylight roof, we can get different results for the indoor environment.
Therefore, I built a base-case model or stereotype model in Grasshopper. It is a loft space with round skylight.
First Goal
Performance Driven Design: Daylighting Simulation and Optimization
This is the original shape of the model. Basically, I have set several parameters for this model, in order to change the size of the skylight, the orientation of the roof, and the rotation angle of the roof.
Let's test DIVA first. We need to know if DIVA can work. Good, the black window pop out. DIVA runs successfully.
This is the result of the first run of DIVA.
Next, I want to do the optimization with Galapagos. As the Galapagos runs, the DIVA keeps calculating. So, the window keeps popping out from time to time.
Finally, we get the result, which is showed below.
Second Goal
Indoor Thermal Comfort Evaluation
The installation of Ladybug+Honeybee requires a lot of preparation. Just like we need to install weavebirds first and kangaroo second, we also need to install a bunch of things before we can have the ladybug and honeybee fly.
To run the energy simulation, first we need to align materials to the model.
To run the energy simulation, first we need to align materials to the model.
Then we need to edit the zone condition and visualize it in Rhino. We also need to have a weather file.
As soon as I click run, a window box pops out. It takes a long time to run the hourly data for a whole year.
After EnergyPlus generates the results, we can move to the next step - "psychrometric chart". We can know from it that more than 90% time is good for people staying inside.
Third Goal
Simple Pattern Design for Walls and Floor
We can use Lunchbox to generate the patterns for the walls. If we want to design a panel, and have that panel all over on to the walls in a certain way, we also need Panelingtools to do that.
wall pattern 1
wall pattern 2
wall pattern 3
wall pattern 4
For Python scripting, I believe it is a way to create new "function icons" in Grasshopper. Without Python script, we can only utilize the existing icons in Grasshopper to do designs, which of course will limit our capability of modeling. With Python, we can create whatever functions we need in a function icon. It will be more flexible for us to do the modeling. However, Python language is not easy to learn. There is a Help Manual that can help people write Python in Grasshopper.
floor tiles 1
floor tiles 3
floor tiles 4
the whole view
Project Movie
In the end, I list these five categories that I may need to learn more after the class.
1. Geometry Modeling and related math, e.g. linear algebra and computer graphics
2. Generative Design with algorithms
3. Computing: visual programming, scripting, textual programming
4. Performance driven design: simulation and optimization
5. BIM: Parametric BIM beyond geoemtry modeling
1. Geometry Modeling and related math, e.g. linear algebra and computer graphics
2. Generative Design with algorithms
3. Computing: visual programming, scripting, textual programming
4. Performance driven design: simulation and optimization
5. BIM: Parametric BIM beyond geoemtry modeling
http://bim-sim.org/ARCH655/lectures.html























7.png)

























